Dispatch System Operation and Maintenance Guide
Picture this: a 911 call drops mid-sentence. Or worse, the entire dispatch system freezes during a city-wide blackout. That’s not just an IT headache; it's a full-blown public safety crisis. This is where a rock-solid operation and maintenance (O&M) strategy comes in—it's the disciplined, proactive work that keeps communication lines open when every second counts.
Why Operation and Maintenance Is Your System’s Lifeline

In the emergency services world, your dispatch system is the central nervous system of your entire operation. If it stumbles, the whole response chain can grind to a halt. Effective O&M isn't just a technical chore you hand off to the IT department; it's the ongoing practice of ensuring this critical infrastructure is always ready and running at peak performance.
Think about it like this: a firefighter doesn't just check their air tank after a call. They run meticulous daily checks on every piece of equipment, from the engine to the ladders. Your dispatch system deserves that exact same level of rigorous attention. After all, it’s the tool that gets that fire engine to the right place at the right time.
A world-class O&M program is built on a few core pillars. When these components work together, they forge an unbreakable chain of reliability that you can count on, even in the most chaotic situations.
This table breaks down the foundational components of a truly resilient O&M strategy.
Core O&M Pillars for Dispatch System Reliability
| Pillar | Core Function | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| People | The trained individuals who understand the system inside and out. | A system administrator who knows how to interpret server error logs and a supervisor who ensures every dispatcher runs their startup checklist before a shift. |
| Processes | The documented, repeatable actions that leave nothing to chance. | A documented procedure for applying critical software updates during off-peak hours or a step-by-step guide for onboarding a new dispatcher. |
| Technology | The tools that automate tasks, monitor system health, and alert you to problems. | A platform like Resgrid that automates personnel scheduling and sends an alert to an IT admin if a server's memory usage spikes. |
These pillars don't work in isolation; they support each other. For instance, a process might dictate a weekly data backup. A designated person (like an IT admin) is responsible for overseeing it. And the technology (an automated script) actually performs the backup and notifies the admin whether it succeeded or failed. This synergy is what prevents a catastrophic data loss.
O&M is the complete lifecycle management of a critical system. Its purpose is to guarantee constant readiness, unwavering accuracy, and absolute reliability when it matters most.
This disciplined approach isn't just for emergency services. The global Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) market was valued at around USD 432.56 billion in 2024 and is expected to keep growing, largely thanks to technologies that enable predictive maintenance. You can read more about the growth of the global MRO market on GlobeNewswire.
By bringing these principles into your agency, you stop treating maintenance as a reactive expense and start treating it for what it really is: a proactive, life-saving investment.
Mastering Your Core O&M Processes
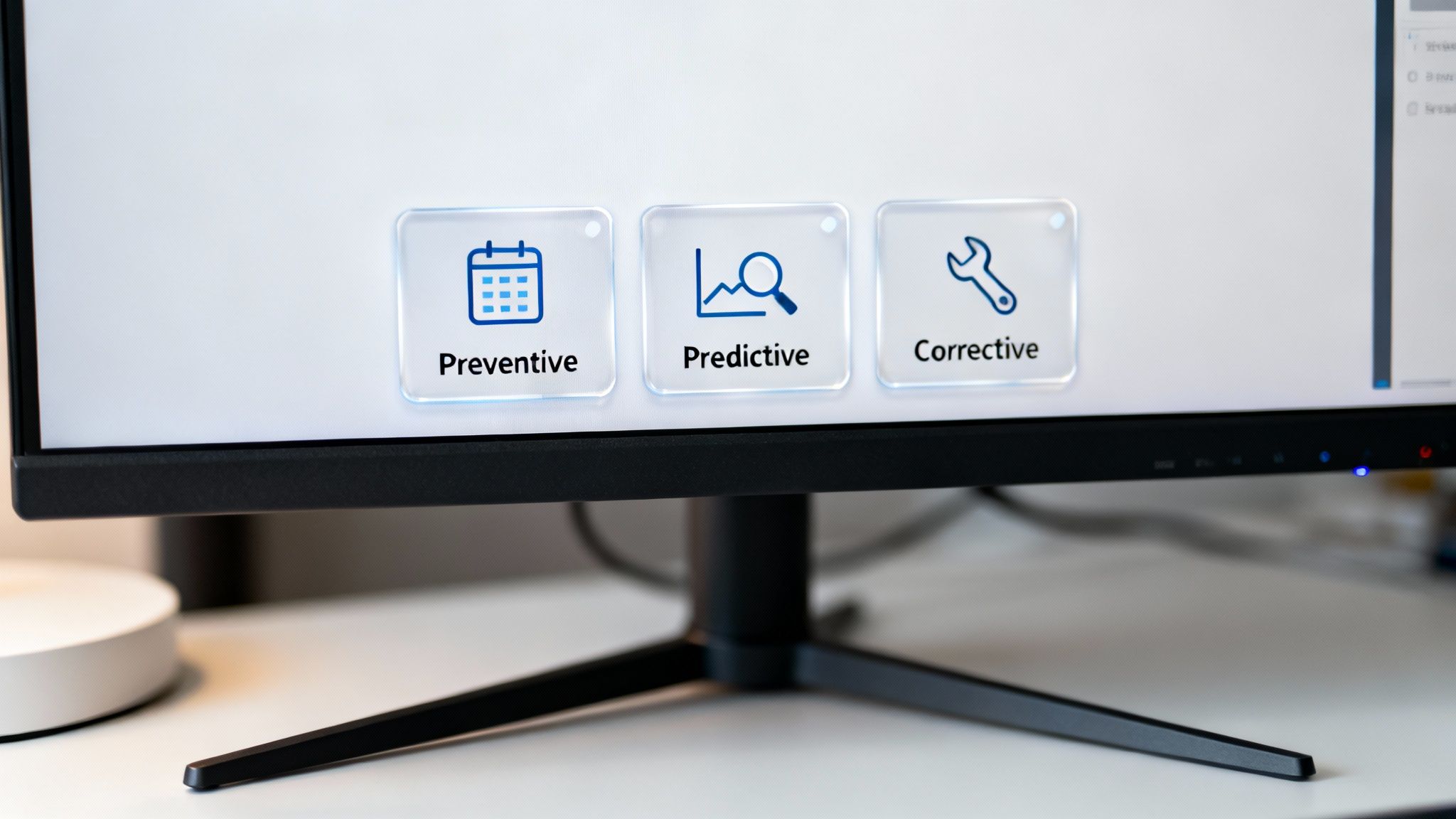

To keep your dispatch system running like a well-oiled machine, you need to get practical. Theory is great, but repeatable, real-world processes are what guarantee reliability when it matters most. A solid operation and maintenance strategy really comes down to three core activities, each with a specific job in protecting your system’s health.
Think of it like taking care of your car. You don’t just drive it until the engine seizes up. You have a routine—oil changes, tire rotations—that keeps it dependable. Your dispatch system is far more critical than your car, and it deserves at least the same level of attention.
Let's break down the three essential processes that make up a rock-solid O&M plan.
Preventive Maintenance: The Scheduled Oil Change
Preventive maintenance is your first and best line of defense. These are the scheduled, proactive tasks you perform to stop problems before they ever start. Just like a routine oil change keeps your car’s engine from locking up, these actions are all about reducing the odds of a catastrophic system failure.
This isn't about fixing what's broken. It's about disciplined upkeep to make sure things never break in the first place. For a dispatch system, this typically includes:
- Regular Software Updates: Applying security patches monthly during a scheduled maintenance window closes vulnerabilities hackers could exploit.
- Scheduled Data Backups: Creating routine, verified copies of your CAD data is your safety net against ransomware or hardware failure.
- Hardware Cleaning: It sounds simple, but physically cleaning server fans and vents prevents overheating—a surprisingly common cause of hardware failure that can lead to unexpected shutdowns.
Predictive Maintenance: The Dashboard Warning Light
Predictive maintenance is a bit more sophisticated. It’s all about using monitoring tools and data to forecast trouble before it grinds your operations to a halt. Think of this as your system’s dashboard warning light—it’s an early alert that something needs attention soon, even if it hasn’t failed yet.
This approach is a game-changer. In fact, studies show that 91% of businesses using predictive maintenance report a drop in repair times and unplanned downtime. In fields that require meticulous record-keeping, tools like medical documentation software show how tracking data can make processes far more efficient and reliable.
Actionable Insight to Save Money: Predictive maintenance prevents expensive emergency repairs. For example, monitoring server disk space and getting an alert when it hits 80% capacity allows you to schedule a cheap, simple cleanup during off-hours. This avoids a full system crash when the disk hits 100%, which would require costly overtime and cause operational chaos.
Let’s look at a practical example. Using a tool like Resgrid, you could set up automated monitoring on your system's API response times. If those times start to creep up—a classic sign of a server getting overloaded—the system can automatically ping your on-call IT admin. This gives them a chance to investigate and fix the root cause before it leads to a system-wide crash that leaves dispatchers in the dark. You can explore how Resgrid makes this possible through its comprehensive dispatch and management features.
Corrective Maintenance: The Roadside Repair
No matter how well you plan, things can still go wrong. Corrective maintenance is what you do when something has already failed. This is the emergency roadside repair—it's unplanned, stressful, and almost always the most expensive kind of maintenance.
While a good O&M plan is designed to minimize these events, you absolutely must have a clear protocol for when they happen. Relying solely on a "break-fix" model is a recipe for disaster in an emergency dispatch environment. It guarantees maximum chaos and cost. A proper corrective maintenance plan should include:
- A Clear Escalation Path: Who do you call at 3 AM on a Sunday when the mapping system fails? Everyone needs to know the exact sequence of contacts.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Step-by-step guides that help technicians find the root cause quickly, without guessing. For instance, a "CAD System Unresponsive" checklist.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Having critical components like hard drives, network cards, and power supplies on-site can turn a days-long outage into a 30-minute fix.
By balancing these three types of maintenance, you build a resilient framework. You shift your organization from a reactive, costly mindset to a proactive, reliable, and far more cost-effective one.
Building Your High-Performance O&M Team
Your operational processes, no matter how perfect on paper, are destined to fail without clear ownership. An operation and maintenance plan is only as good as the team tasked with carrying it out. When roles are fuzzy, accountability evaporates, and small hiccups can quickly spiral into major crises simply because nobody knew it was their job to step in.
Think of your O&M team like the pit crew for a race car. Every person has a specific, vital role. The tire changer isn't thinking about refueling, and the jack man isn't wiping down the windshield. This specialization is what allows them to perform complex tasks with incredible speed and precision, keeping the car—or your dispatch system—running at its absolute peak.
Bringing that same kind of structure into your agency is fundamental. It eliminates the "who's on first?" guesswork during high-pressure situations and guarantees that every aspect of your system's health, from daily checks to emergency fixes, has a designated owner.
Defining Your Core O&M Roles
Just like that pit crew, your team needs distinct roles with crystal-clear responsibilities. The job titles might change from one agency to another, but the functions are universal. A well-structured team ensures that nothing ever falls through the cracks, creating a layered defense against system failure.
These roles need to work in concert to cover the full spectrum of O&M duties:
-
System Administrator: This is your chief mechanic. The administrator is on the hook for the system's core health, handling things like software updates, server resource management, backups, and configuring the underlying infrastructure. Practical Example: They are responsible for applying the monthly Windows Server security patches and verifying that the nightly database backup completed successfully.
-
Support Specialist: Think of this person as the first responder for user issues. When a dispatcher can't log in or a terminal gets sluggish, the support specialist is the first call. They handle the initial troubleshooting, document the problem, and solve common issues. Practical Example: They reset a dispatcher's forgotten password or reinstall a malfunctioning software client on a workstation.
-
Dispatch Supervisor: This role is the crew chief. The supervisor isn't necessarily a deep technical expert, but they are a procedural one. They ensure dispatchers are actually following the O&M protocols, like running through their daily startup checklists and correctly reporting any weird behavior they see. Practical Example: They ensure the on-duty dispatcher completes the "Start of Shift" checklist in the system and signs off on it.
Creating an Unbreakable Chain of Command
Knowing who does what is only half the battle. The other, arguably more critical half, is defining what happens when a problem is too big for one person to handle. This is where a documented escalation path is absolutely essential. It's a simple, step-by-step guide that dictates who to call and when, preventing confusion and saving precious time when things go sideways.
A documented escalation path turns chaos into order. It ensures that a critical issue is never left sitting in an inbox and always reaches the person with the authority and expertise to solve it, fast.
For instance, a support specialist might get a call about a single slow computer. Their protocol is to try a standard reboot. If that doesn't fix it, the escalation path tells them to immediately notify the System Administrator. If the admin discovers it's a network-wide problem, the path might then require them to loop in the agency's director. This simple, documented flow keeps things moving and prevents bottlenecks.
Actionable Insight to Save Money
Here’s where you turn this structure into a powerful cost-saving tool. Using a platform like Resgrid, you can build these real-world roles directly into the software itself. By configuring user permissions, you give each team member access only to the functions they need to do their job.
This one action can have a massive financial impact. A Dispatch Supervisor can view reports but can't change critical system settings. A Support Specialist can manage user tickets but has no access to sensitive server configurations. This dramatically cuts down on the risk of human error—a leading cause of expensive outages. By preventing one accidental deletion of a user group or an incorrect network change, you save yourself from the crippling downtime and emergency repair costs that always follow.
Creating Your O&M Schedule and Checklists
A high-performance team and solid processes are essential, but without a schedule, even the best intentions can fall flat. This is where we turn theory into consistent, reliable action. Effective operation and maintenance lives and dies by routine, and the best way to build that routine is through clear, repeatable checklists and a predictable schedule.
These aren't just bureaucratic hurdles or boxes to tick. Think of them as your system’s first line of defense—a daily, weekly, and monthly health check that catches minor issues before they have a chance to become catastrophic failures. They instill discipline and ensure that critical tasks are never overlooked, even during the most chaotic shifts.
Building Your Maintenance Cadence
The key is to create a rhythm of maintenance tasks by sorting them based on how often they need to get done. This ensures you cover everything from immediate daily needs to longer-term system health without burning out your team. Each frequency has a specific job in your overall O&M strategy.
Unplanned downtime is a massive headache for organizations of all sizes. Research shows that aging equipment is the top culprit for 42% of facilities, followed by straight-up mechanical failure (21%) and simple operator error (11%). A structured O&M schedule is your best weapon against these common problems. You can dig into more of the causes of unplanned downtime on Sockeye.
A tiered schedule gives you a framework for proactive care, turning maintenance from a reactive scramble into a predictable workflow.
A well-structured schedule provides a clear roadmap for your team. Here’s a sample template that shows how you might organize tasks by frequency to ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
Sample O&M Maintenance Schedule
| Frequency | Task Description | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Verify all dispatch terminals are online and responsive. | Ensure every dispatcher has a functional workstation at the start of their shift to prevent operational delays. |
| Daily | Confirm automated backup from the previous night completed successfully. | Guarantee data integrity and the ability to restore the system in case of a critical failure. |
| Weekly | Check server logs for unusual error patterns or warnings. | Identify emerging software or hardware issues before they impact system performance or cause an outage. |
| Monthly | Review and audit user accounts, permissions, and access levels. | Enhance security by removing old accounts and ensuring active users have only the permissions they need. |
| Monthly | Perform system patching and reboot servers during a scheduled, off-peak window. | Apply critical security updates to protect against vulnerabilities and maintain system stability. |
This table is just a starting point, of course. You'll want to tailor it to your specific hardware, software, and operational demands.
From Manual Lists to Automated Accountability
While paper checklists are a decent start, their biggest weakness is human error. A busy shift, a distracting event, or just plain forgetfulness can lead to a missed check, leaving a dangerous gap in your defenses. This is where automation becomes your most valuable, money-saving ally.
Actionable Insight to Save Money: The true cost of a missed checklist isn't the paper it's printed on; it's the multi-thousand-dollar emergency repair bill for a failure that could have been prevented. For example, automating a daily backup check prevents a scenario where backups have been failing silently for weeks, which would lead to catastrophic data loss and huge recovery costs after a server failure.
Instead of relying on memory and paper, you can use a tool like Resgrid to digitize and automate this entire process. For instance, you can set up recurring tasks or automated "calls" that are assigned to specific roles or individuals at just the right time.
- A daily "call" can be automatically generated at 7 AM for the on-duty supervisor to confirm all terminals are online.
- A weekly task can be assigned to the IT admin to review server logs every Friday.
- A monthly alert can remind the System Administrator to conduct the user account audit.
This does more than just send reminders. It creates a permanent, auditable trail. Every completed task is logged with a timestamp and the user who did it, which is invaluable for compliance reviews and internal accountability. It transforms your O&M checklists from a passive document into an active, intelligent system that drives action and prevents costly failures. You can see how Resgrid makes these workflows happen by exploring the various apps and integrations available on our platform.
Tracking KPIs and Managing Incidents
You can't improve what you don't measure. In a high-stakes environment like emergency dispatch, "hoping for the best" isn't a strategy—it's a liability. A disciplined operation and maintenance plan lives and dies by the data it collects. This is where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) become your command center.
Think of KPIs as the vital signs monitor for your dispatch system. Just like a doctor wouldn't treat a patient without checking their heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, you can't manage your system's health without a clear view of its core metrics.
These numbers cut through the noise, giving you a real-time, objective look at how everything is performing. They’re the first to tell you when trouble is brewing, long before it becomes a full-blown crisis.
Your System’s Vital Signs
While you can track dozens of metrics, a few core KPIs tell you almost everything you need to know. Focusing on these will give you the clearest picture of your operational readiness.
-
System Uptime: This is the big one. It's the percentage of time your system is online and fully functional. The gold standard in this field is 99.999%, often called "five nines" uptime. That translates to just over five minutes of unplanned downtime in an entire year.
-
Software Response Time: How fast does the system react when a dispatcher clicks a button? This KPI tracks the lag between a user action—like looking up a record or sending a unit—and the system's response. Practical Example: If the time to run a vehicle plate search creeps up from 0.5 seconds to 3 seconds, it's a clear warning of a potential database or network issue.
-
Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): When things inevitably break, this metric measures the average time it takes to fix the problem, from the initial alert to the "all clear." A low MTTR is a direct reflection of a well-oiled O&M machine.
A structured maintenance schedule is what keeps these KPIs healthy. It’s all about being proactive, not reactive.
This workflow shows how consistent daily checks, weekly reviews, and deeper monthly maintenance build a powerful defense against system issues, keeping your vital signs strong.
Your Step-by-Step Incident Response Plan
Knowing your KPIs are in the red is one thing. Knowing exactly what to do about it is something else entirely. A documented incident response plan is what separates a minor hiccup from a major outage. It turns chaos into a calm, repeatable process.
A solid plan has a clear lifecycle:
- Detect: The problem first surfaces, either through an automated monitoring alert (like a server error spike) or a report from a user.
- Log: The incident is officially recorded. This creates a timestamped ticket with a description of the problem and its initial severity.
- Diagnose: The on-call technician digs in to find the root cause. This isn’t just about what broke, but why it broke.
- Escalate: If the first responder is stuck, they follow a clear chain of command to loop in senior engineers or specialists.
- Resolve: The team implements a fix. This could be as simple as rebooting a server or as complex as deploying a hotfix patch.
- Review: Once the dust settles, the team holds a post-mortem. They document what happened, what went right, and what they can do better next time. This is how you learn and improve.
To get the job done right, your team needs the right tools. During the critical "Diagnose" phase, for example, having access to essential network diagnostic utilities can make the difference between a quick fix and a prolonged outage.
Actionable Insight to Save Money: Automating the first steps of incident response saves critical minutes, which translates directly into cost savings. A system that automatically logs an issue and notifies the right person shaves time off your MTTR. Reducing resolution time from 60 minutes to 30 minutes for a critical outage can save thousands in operational costs, lost productivity, and potential SLA penalties.
With a platform like Resgrid, you can automate big chunks of this workflow. For instance, an automated monitor can spot a high API error rate (Detect). It can then be set up to instantly create an incident in Resgrid (Log) and automatically notify the on-call system administrator (Escalate).
This automated handoff eliminates the delays of manual phone calls and emails, letting your team jump straight into diagnosis and resolution. This simple automation can dramatically lower your MTTR, minimize the impact on operations, and ultimately save your organization money by stopping small problems before they become catastrophes.
Securing Your System with O&M Best Practices
In the world of emergency services, security isn't just an IT concern—it's a fundamental part of our legal and ethical duty. We handle incredibly sensitive information every day, from medical records to law enforcement data. Your operation and maintenance plan is what turns compliance rules like HIPAA and CJIS from abstract requirements into concrete, daily actions that protect your agency and the people you serve.
Think of your O&M plan as the constant, vigilant security detail for your data. It’s not about a one-time setup; it's the disciplined, routine work that builds a real defense.
These everyday tasks are your first line of defense. When you run monthly software patches, you're not just improving performance—you're closing the exact security holes that hackers look for. Likewise, doing a weekly audit of who accessed what data isn't just busywork. It creates an undeniable record that can be a lifesaver during a compliance review.
From Maintenance Tasks to Risk Mitigation
Every single item on your O&M checklist is, at its core, a form of risk management. When you start looking at maintenance through a security lens, its true importance becomes crystal clear.
- User Account Audits: How many old or unused accounts are sitting in your system? Each one is a potential backdoor. Practical Example: A quarterly audit might reveal an account for an employee who left six months ago. Deactivating it immediately closes a significant security gap.
- Data Backup Verification: Running a backup is only half the job. Proving you can actually restore from it is your ultimate safety net against a ransomware attack. Practical Example: Monthly, restore a single non-critical file from backup to a test location to confirm the data is readable and not corrupt.
- Permission Reviews: The principle of least privilege is your best friend. Making sure dispatchers and admins only have the access they absolutely need prevents both accidental data leaks and malicious internal threats. Practical Example: A yearly review confirms dispatchers can create and manage calls but cannot access system configuration settings.
Actionable Insight to Save Money: The cost of a solid maintenance program is a drop in the bucket compared to the financial and reputational damage of a single data breach. Proactively running a user account audit costs a few hours of staff time. Failing to do so could lead to a breach via a forgotten account, resulting in fines that can easily run into the hundreds of thousands of dollars, not to mention legal fees and recovery costs.
Integrating Compliance into Your Workflow
The trick is to weave security and compliance into the fabric of your daily operations, so it doesn't feel like a separate, overwhelming chore. This is where having the right tools can completely change the game, turning complex mandates into simple, automated processes.
A system like Resgrid lets you build these best practices right into your dispatch environment. For example, you can use its detailed permission controls to enforce the principle of least privilege with just a few clicks, ensuring team members only see the information directly relevant to their role.
Better yet, secure audit trails automatically log every critical action inside the system. This gives you a permanent, easily searchable record for any compliance check. Instead of scrambling to pull manual logs for an audit, you can generate a comprehensive report in minutes. This approach doesn't just simplify compliance; it makes your entire operation more secure by default. When you have this level of control over your data and access, you can be genuinely confident in your agency's security.
Answering Your Operation and Maintenance Questions
Even with the best plan in hand, real-world questions always pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common hurdles agencies face when they start getting serious about operation and maintenance. Here are some straight answers to help you get started, save money, and make your system more reliable from day one.
How Can We Start an O&M Plan with a Limited Budget?
You don’t need a massive budget to get an effective O&M program off the ground. The secret is to start small and focus on high-impact, low-cost actions that show immediate value.
Begin with simple daily and weekly manual checklists. Practical Example: Create a one-page "Start of Shift" checklist for dispatchers to verify their phone, radio, and CAD login are all working. This costs nothing but immediately prevents shift-change delays. Take a hard look at your current setup, document everything, and pinpoint the single most common reason things go wrong. Aim your first preventive efforts right there.
Actionable Insight to Save Money: The goal is to score early wins. By implementing a simple weekly server reboot schedule during off-hours, you might reduce system freezes by 50%. This demonstrates a measurable drop in minor incidents, building a rock-solid case for future investment in more sophisticated tools and automation. It proves that spending a little staff time now saves a lot in emergency costs later.
What Is the Biggest Mistake to Avoid in Dispatch System Maintenance?
The single biggest—and most costly—mistake is the "set it and forget it" mindset. Thinking of your dispatch system as something that only needs attention when it’s actively broken is a recipe for disaster. This reactive approach guarantees you'll face expensive downtime, be forced to pay for emergency repairs, and even risk losing critical data.
Proactive, scheduled maintenance isn't just an optional expense; it's a fundamental part of running your operation. A very close second is skimping on documentation. When a system goes down in the middle of a crisis, a lack of clear documentation can turn a simple ten-minute fix into a multi-hour scramble, making a bad situation much worse.
How Can We Measure the ROI of Our O&M Efforts?
Measuring the return on your O&M investment comes down to one thing: tracking the costs you didn't have to pay. Your most powerful metric here is the reduction in unplanned downtime.
First, you need to calculate what one hour of downtime actually costs your agency. Factor in everything—overtime for staff, lost productivity, and even potential compliance fines. Once you have that number, you can compare your total downtime hours before and after you put your O&M plan into action.
Practical Example to Save Money: Let's say one hour of downtime costs your agency $5,000. Before your O&M plan, you averaged 4 hours of unplanned downtime per month ($20,000 cost). After implementing daily checks and monthly patching, you reduce that to just 30 minutes per month ($2,500 cost). You can now definitively show an ROI of $17,500 per month from your O&M efforts, easily justifying the time and resources spent.
Ready to build a resilient, efficient, and cost-effective operation and maintenance strategy? Resgrid gives you the tools to automate checklists, track incidents, and manage your team all in one place. See how you can prevent costly downtime and improve your operational readiness by visiting https://resgrid.com.

